AKTUELLES
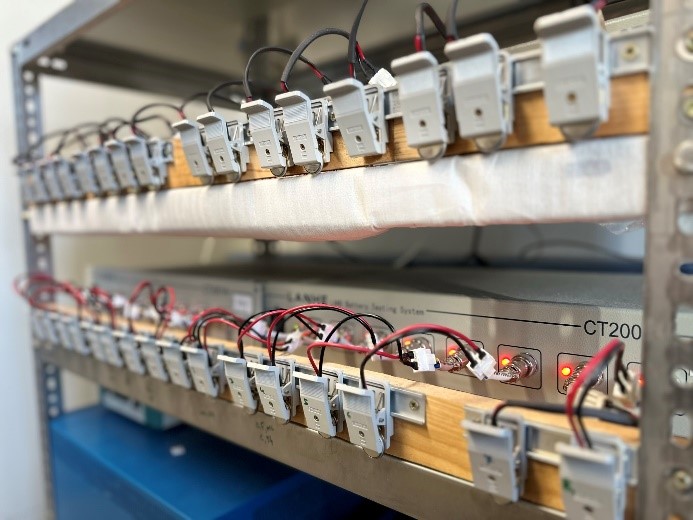
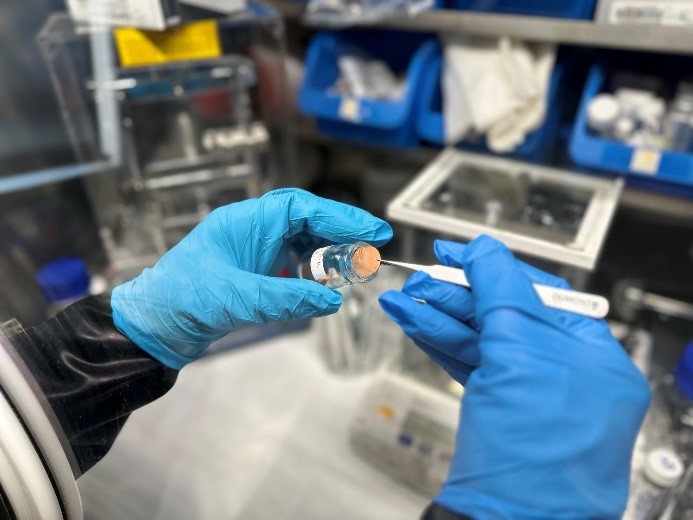
18.04.2024Erstaunlicher Durchbruch in der Batterietechnologie durch innovative Kathoden auf SchwefelbasisEin Forschungsteam der Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin hat einen entscheidenden Durchbruch in der Batterietechnologie erzielt. Unter der Leitung des IRIS Adlershof Mitglieds Prof. Dr. Michael J. Bojdys wurde eine innovative schwefelbasierte Kathode entwickelt, die die Nutzung von umweltfreundlicheren und nachhaltigeren Materialien in Lithium-Ionen-Batterien ermöglicht. Die Ergebnisse dieser bahnbrechenden Studie wurden am 15. April 2024 in der renommierten Fachzeitschrift Angewandte Chemie veröffentlicht.
Die neue Technologie, die Schwefel in einem speziellen mikroporösen Imin-Polymernetzwerk verkapselt, zeigt nicht nur eine erhöhte Leistungsfähigkeit und Lebensdauer von Batterien, sondern adressiert auch das kritische Problem der Ressourcenknappheit bei herkömmlichen Batteriematerialien wie Kobalt. „Diese Entwicklung könnte die Art und Weise, wie wir Energie speichern und nutzen, grundlegend verändern und stellt einen wichtigen Schritt in Richtung einer nachhaltigeren Zukunft dar“, erklärte Prof. Bojdys.
Prof. Dr. Michael J. Bojdys ist ein Experte auf dem Gebiet der nachhaltigen Energiematerialien und trägt im Rahmen der BMBF-Initiative “GreenCHEM” dazu bei, die chemische Industrie in der Berliner Hauptstadtregion durch die Verbindung von Wissenschaft und Industrie zu einer auf nachhaltigen Rohstoffen basierenden Kreislaufwirtschaft zu transformieren. Für weitere Informationen und Details zur Studie stehen Ihnen Prof. Dr. Michael J. Bojdys und sein Team, Barbora Balcarova und Guiping Li, als wissenschaftliche Ansprechpartner zur Verfügung. Sie können unter der E-Mail-Adresse michael.janus.bojdyshu-berlin.de oder via bojdyslab.org kontaktiert werden. 28.03.2024Automated calculation of surface properties in crystalsThe surface properties of complex crystalline materials can be calculated reliably and automatically using only the fundamental laws of physics, thanks to a new computer-based method. Writing in the journal npj computational materials, researchers from the University of Oldenburg in Germany outline how their method could speed up the search for new materials for important technologies such as photovoltaics, batteries or data transmission.
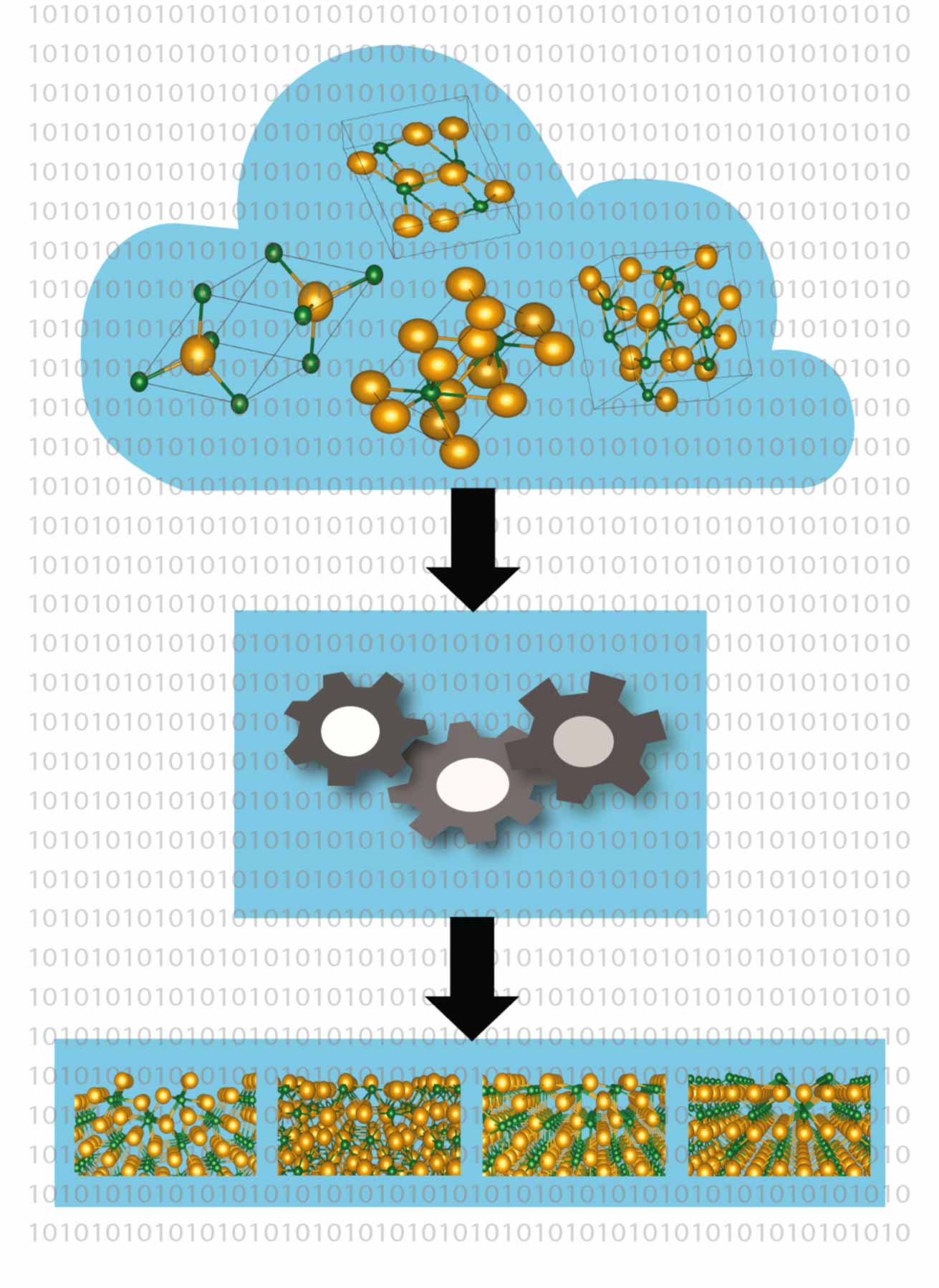
Computer-aided methods are becoming an increasingly powerful tooI in the search for new materials for key technologies such as photovoltaics, batteries and data transmission. Member of IRIS Adlershof Prof. Dr. Caterina Cocchi and Holger-Dietrich Saßnick from the University of Oldenburg’s Institute of Physics have now developed a high-throughput automatised method to calculate the surface properties of crystalline materials starting directly at the level of established laws of physics (first principles). In an article published in the journal npj computational materials, they report that this can speed up the search for relevant materials for applications in key areas such as the energy sector. They also plan to combine the method with artificial intelligence and machine learning techniques to further accelerate the process. So far similar methods have focused on bulk materials rather than surfaces, the two physicists explain. “All the relevant processes for energy conversion, production, and storage occur on surfaces,” says Cocchi, who heads the Theoretical Solid State Physics research group at the University of Oldenburg. However, calculating the material properties of surfaces is far more challenging than for complete crystals because the surface facets often have a complex structure due to factors such as defects in the crystal structure or the uneven growth of a crystal, she explains. This complexity poses problems for researchers in the field of materials science: “It is often not possible to clearly determine the properties of samples in experiments," says Cocchi. This motivated Cocchi and her colleague Saßnick to develop an automated procedure for high-quality screening of the characteristics of new compounds. The result of their work was incorporated into the aim2dat computer programme, which only requires the chemical composition of a compound as input. The information about the crystal’s structure is extracted from existing databases. The software then calculates the conditions under which the surface of the material is chemically stable. In a second step it determines key properties, in particular the energy required to excite electrons into conduction states or detach themselves from a surface. This parameter plays an important role in materials that convert solar energy into electricity, for example. "We don't make any assumptions in our calculations; we use only the fundamental equations of quantum mechanics, which is why our results are very reliable," Cocchi explains. The two scientists demonstrated the applicability of the method using the semiconductor cesium telluride. The crystals of this material, which is used as an electron source in particle accelerators, can occur in four different forms. “The composition and quality of the material samples are difficult to control in experiments,” notes Saßnick. Nevertheless, the Oldenburg researchers were able to perform a detailed analysis of the physical properties for the different configurations of the caesium telluride crystals. Cocchi and Saßnick have embedded the software in a publicly accessible programme library so that other researchers can also use and improve the procedure. “Our method has great potential as a tool for discovering new materials – and in particular physically and structurally complex solids – for all kinds of applications in the energy sector," says Cocchi. Originalpublikation:Saßnick, HD., Cocchi, C. “Automated analysis of surface facets: the example of cesium telluride.” npj Computational Materials 10, 38 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41524-024-01224-7
|